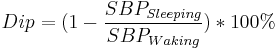Ambulatory blood pressure
| Ambulatory blood pressure | |
|---|---|
| Diagnostics | |
| MeSH | D018660 |
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) measures blood pressure at regular intervals [1]. It is believed to be able to reduce the white coat hypertension effect in which a patient's blood pressure is elevated during the examination process due to nervousness and anxiety caused by being in a clinical setting. Out-of-office measurements are highly recommended as an adjunct to office measurements by almost all hypertension organizations.
Contents |
Nocturnal hypertension
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring allows blood pressure to be intermittently monitored during sleep, and is useful to determine whether the patient is a dipper or non-dipper--that is to say whether or not blood pressure falls at night compared to daytime values. A night time fall is normal. It correlates with relationship depth but other factors such as sleep quality, age, hypertensive status, marital status, and social network support.[2] Absence of a night time dip is associated with poorer health outcomes, including increased mortality in one recent study.[3] In addition, nocturnal hypertension is associated with end organ damage[4] and is a much better indicator than the daytime blood pressure reading.
Target organ damage
It has been shown that end-organ damages related to hypertension, such as left ventricular hypertrophy, narrowing of the retinal arteries are more strongly associated with ABPM than with a clinical BP measurement, the reason being clinical BP measurement are referred to the marked variability of BP measurement and white coat effect [5].
Morning surge
The day-night time fluctuates with values rising in the daytime and falling after midnight. With these changes, its possible to calculate the BP dip, with categories such as non-dipper (<10%), dipper, extreme dipper, and reverse dipper. Independent studies have shown that for subject with blunted or abolished fall dip and abnormal ABP result in higher incidences of LV hypertrophy and CV mortality [6]. According to the American Heart Association, an excessive morning blood pressure surge is a predictor of stroke in elderly people with high blood pressure [7][8].
This is based on the American Heart Association's calculation, using systolic blood pressure (SBP):
| Range | Class |
|---|---|
| <0% | Reverse Dipper |
| 0% - 10% | Non-Dipper |
| 10% - 20% | Dipper |
| >20% | Extreme Dipper |
Blood pressure variability
24-hour, non-invasive ambulatory blood pressure monitoring allows estimates of BP variability.
International Research
ARTEMIS http://www.artemisnet.org](international Ambulatory blood pressure Registry: TEleMonitoring of hypertension and cardiovascular rISk project) is the first International Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring Registry aiming at assessing the actual degree of blood pressure and cardiovascular risk control of hypertensive patients followed by doctors all over Europe. The project is based on telemonitoring on BP through a web-based telemedicine service (MOREPRESS at www.morepress.net).
References
- ^ Validation of the Microlife WatchBP O3 device for clinic, home and ambulatory blood pressure measurement, according to the International Protocol
- ^ Holt-Lunstad J, Jones BQ, Birmingham W. (2009).The influence of close relationships on nocturnal blood pressure dipping. Int J Psychophysiol. 71(3):211-7. doi:10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2008.09.008 PMID 18930771
- ^ Minutolo R, Agarwal R, Borrelli S, Chiodini P, et al (2011). Prognostic role of ambulatory blood pressure measurement in patients with nondialysis chronic kidney disease. Arch Intern Med. 171(12):1090-8.
- ^ Use and interpretation of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring: recommendations of the British Hypertension Society
- ^ Verdecchia P, Angeli F, Gattobigio R (2004). "Clinical usefulness of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring". J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 15 Suppl 1: S30–3. PMID 14684668. http://jasn.asnjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=14684668. Retrieved 2008-12-01.
- ^ Monday Morning Surge in Blood Pressure May Lead to Increase in Cardiovascular Events, American Heart Association
- ^ Morning surge in blood pressure linked to strokes in elderly
- ^ Stroke Prognosis and Abnormal Nocturnal Blood Pressure Falls in Older Hypertensives
External links
- ARTEMIS, international Ambulatory blood pressure Registry: TEleMonitoring of hypertension and cardiovascular rISk project
- Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring, Medical Journal of Australia